Complex Numbers | ||
| ||
Introduction | ||
In this section, you will learn how to perform a variety of operations with complex numbers. Here are the sections within this lesson:
To understand this information in the following sections, you must understand how to simplify a radical. Use this lesson to learn more before continuing.
|
In order to understand what a complex number is, we first have to understand what imaginary numbers are. Let’s explore some square roots, like these:
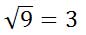
It is equal to three because 3-squared is equal to 9.
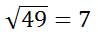
It is equal to seven because 7-squared is equal to 49. Try to take the square root here:
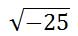
Five times five is 25. Negative five times negative five is 25. So, there is no real number solution for this problem. This is why we will have to approach it like this.
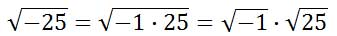
We know that the square root of 25 is 5, but there is no real number solution for the square root of negative 1. Mathematicians call this value imaginary and label it with an ‘i’ like so.
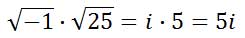
The negative under the square root results in the ‘i.’
| |
A complex number is a number that has a real part and an imaginary part. They are written in this form:
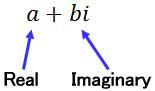
A real number can be a fraction, decimal value, or an integer. The real part is represented with the value ‘a.’ An imaginary number is a value that contains a negative under a square root, which is designated as the value ‘b’ in our complex number. Here are three imaginary numbers, separated by commas:
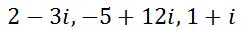
| |
Adding complex numbers is something that can be done by high school algebra students who understand like terms. Say we had to add these two complex numbers.
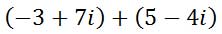
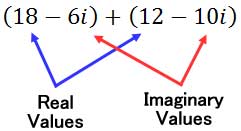
We simply add the real parts together and then add the imaginary parts together, keeping the two separate.
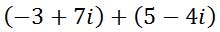
Next, write their sums accordingly.
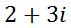
Here is another example.
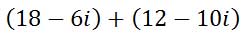
Add like terms.
Here is the solution.
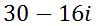
View our video and try our quizmaster on this lesson.
| |
Let’s take a look at a problem.
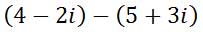
To subtract, take the opposite of the second complex number.
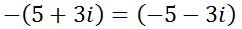
Doing so will change the problem into an addition problem.
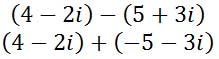
Now, combine real values together and combine imaginary values together, like was done for the addition section above. Here is the solution.
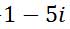
View our video and try our quizmaster on this lesson.
| |
Following sections within this page will deal with powers of 'i,' like i2, i3, or in, where the n-value can be either positive or negative integers. To prepare for multiplication and division of complex numbers, view this vital video.
| |
Multiplying complex numbers requires more detail than adding or subtracting complex numbers. Here is a multiplication problem.
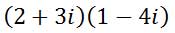
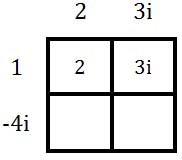
To multiply these complex numbers, we will use a multiplication table. Doing so helps us to organize our information. We will place the first complex number along the top of the table and the left side of the table.
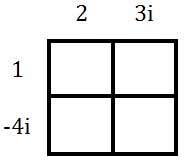
Now, we need to start multiplying columns times rows. We will multiply 1 times 2.
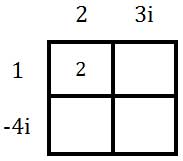
Next, multiply 1 times 3i.
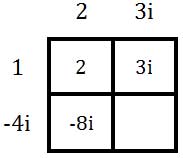
Next, multiply 2 times -4i.
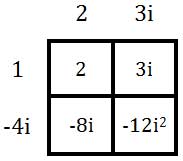
Last, multiply -4i times 3i.
Next, let’s arrange all the terms together from our table.
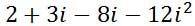
We now need to make a substitution for i-squared. I-squared is equal to -1. Making the substitution looks like this.
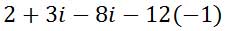
We can clean up the expression as follows.
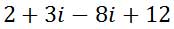
Last, let’s combine like terms.
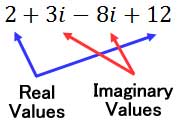
Here is the final solution.
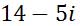
Here is another example.
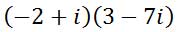
Here is the set-up for using a multiplication table.
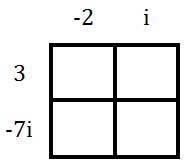
Here is the table filled in.
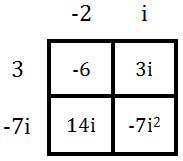
Here are the terms from the table and the subsequent steps for simplifying the expression.
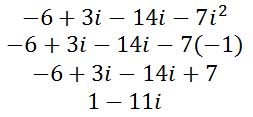
Watch our video and try our quizmaster on this lesson.
| |
Dividing complex numbers is a bit technical. To deal with it, we have to deal with something called conjugates. A conjugate of a complex number is gained by taking the opposite of the imaginary part of a complex number. Here is a table that has complex numbers and their corresponding conjugates.
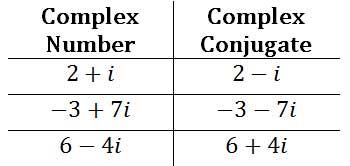
When conjugates are multiplied together, something interesting happens. Here is an example of two complex conjugates and we are going to multiply them.
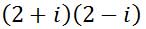
Here is a table already set up and filled.
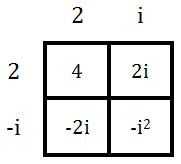
Here are the terms from the table.
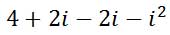
Now, we will simplify the expression.
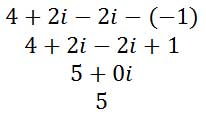
Every time we multiply complex conjugates, the imaginary term cancels and we obtain a real answer. We will make use of this interesting phenomenon when we divide complex numbers. Here is an example of a division problem.
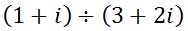
The same problem can be written vertically, like a fraction.
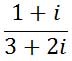
To divide these complex umbers, we are going to employ a slight trick. The only way to clean up this division problem is to cancel the imaginary numbers in the denominator. We will do so by multiplying the denominator by its complex conjugate, 3 – 2i, as follows.
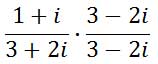
We multiplied the numerator by the same amount so as not to alter the value of the original fraction. When multiplying fractions, multiply left-to-right.
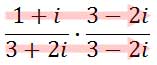
To multiply, two tables need to be set up – one for multiplying the numerators and the other for multiplying the denominators, like so.
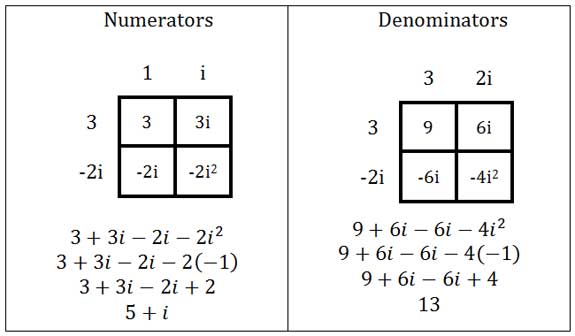
Let’s now place these expressions in a fraction where they belong.
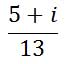
Last, we need to divide the entire numerator by 13.
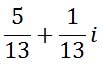
Watch our video on this lesson.
| |
Imaginary numbers have a great deal of significance within aerodynamics, specifically the shapes of wings on aircrafts. Imaginary numbers can be used to determine the shapes which maximize lift. Physicists use the graphs of complex numbers to explain the probable placement of particles within nuclear reactions. When two-dimensional distortions, like rotations, reflections, and dilations, are important, the positions of objects can be found using complex numbers.
Electrical engineers use imaginary numbers when dealing with competing sine wave interactions. The sine waves can be handled using complex numbers to determine flows of current.
| |
Watch these instructional videos to understand the lessons above.
| |
Try our interactive quizzes to determine if you understand the lessons above.
| |
Try this activity related to the lessons above.
| |
Try these lessons, which are closely related to the lesson above.
| |
 esson:
esson:  ideo:
ideo:  uiz:
uiz:  ctivity:
ctivity: